M.2 (formerly known as NGFF) is a small form factor card and connector that supports applications such as Wi-Fi, WWAN, USB, PCIe & SATA, as defined in the PCI-SIG M.2 Specification (see www.pcisig.com).

- An M.2 card with a SATA interface will typically be an SSD, suitable for very thin devices such as Ultrabooks or tablets
- SATA M.2 is described in the SATA v3.2 Specification.
- Detailed M.2 specifications are contained in the PCI-SIG M.2 Specification (see www.pcisig.com)

- M.2 cards are available in single-sided or double-sided versions
SATA-IO, the SNIA Solid State Storage Initiative and the NVM Express Organization combined to host the webcast, "All About M.2 SSDs". The webcast provided a technical overview of M.2, including the following topics:
- Recent trends in the M.2 SSD market
- M.2 cards and connection schemes
- NVM Express as it relates to M.2 SSDs
- Throughput, latency, and IOPS performance of M.2 SSDs
Check out a replay of the webcast here: https://www.brighttalk.com/webcast/663/112647
To download "All About M.2 SSDs" webcast slides, click here.
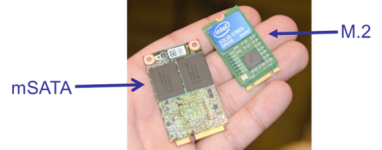
M.2 - mSATA Comparison
Where mSATA took advantage of an existing form-factor and connector, M.2 has been designed to maximize the usage of the card space, while minimizing the footprint.
| mSATA | M.2 | |
| Width (mm) | 30 | 22 |
| Length (mm) | 50.95 | 30, 42, 60, 80, 110 |
|
PCB Space - L x W (mm) |
1528.5 | 660, 924, 1320, 1760, 2420 |